



Next: Initializing the variables
Up: The script sdp.m
Previous: Preparing the data
It is important to set the parameters correctly in order to take full
advantage of the codes. Particular attention should be paid to the
termination parameters 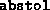 ,
, 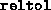 and
and 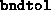 , for which
appropriate values are quite problem dependent.
All the parameters are set to their default values by calling the
routine setpars.m. The default values demand high accuracy;
the number of iterations required to meet the termination criteria is reduced
by requesting less accurate solutions.
, for which
appropriate values are quite problem dependent.
All the parameters are set to their default values by calling the
routine setpars.m. The default values demand high accuracy;
the number of iterations required to meet the termination criteria is reduced
by requesting less accurate solutions.

- (Default value = 100)
The maximum number of iterations which may be taken by the algorithm.
If  (see below), then explicitly setting
(see below), then explicitly setting 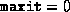 before calling the solver results in just data validation alone.
before calling the solver results in just data validation alone.
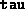
- (Default value = 0.999)
The fraction of the step to
the boundary (of the positive semidefinite cone) taken by the
algorithm. This choice leads to fast convergence and is generally
reliable, but may occasionally lead to failures due to short steps
(see below). In many cases, the quantity 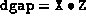 is
reduced by approximately a factor of
is
reduced by approximately a factor of 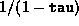 per iteration in
the last few iterations.
per iteration in
the last few iterations.
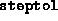
- (Default value =
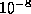 )
)
Tolerance on the
primal and the dual steplengths. If either one of these drops below
 , the algorithm terminates. If the infeasibility or
dgap is large, it is recommended to try restarting with
either a reduced value of
, the algorithm terminates. If the infeasibility or
dgap is large, it is recommended to try restarting with
either a reduced value of  or with
or with  and
and 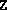 set to
larger multiples of the identity. This is done automatically when the
driver script sdp.m is used, but is not done if the the
driver script is bypassed with a direct call to the function
fsdp.m.
set to
larger multiples of the identity. This is done automatically when the
driver script sdp.m is used, but is not done if the the
driver script is bypassed with a direct call to the function
fsdp.m.
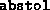
- (Default value =
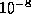 )
)
Absolute tolerance on the total error, imposing the condition
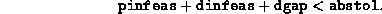
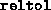
- (Default value =
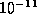 )
)
Relative tolerance on the total error, imposing the condition
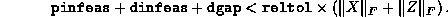
reltol is usually set to a value smaller than that of
abstol. Successful termination takes place when both
the absolute and relative conditions are satisfied. Either one can be
relaxed by making the corresponding tolerance large.
- (Default value = 100)
Tolerance on progress; this parameter, in conjunction with
 (see below), determines when the algorithm
should terminate if significant progress is not taking place.
If
(see below), determines when the algorithm
should terminate if significant progress is not taking place.
If 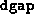 is less than the previous value of
is less than the previous value of 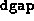 divided by
divided by
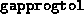 , then the progress is considered ``sufficient''. This
check is performed only when
, then the progress is considered ``sufficient''. This
check is performed only when 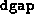 has been reduced below
has been reduced below 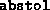 .
.

- (Default value = 5)
Tolerance on progress;
this parameter, in conjunction with 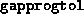 (see above),
determines when the algorithm should terminate if significant progress
is not taking place. If the new
(see above),
determines when the algorithm should terminate if significant progress
is not taking place. If the new  is less than
is less than
 times the previous
times the previous  , or the new
, or the new 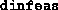 is
less than
is
less than  times the previous
times the previous 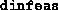 , then the loss
of feasibility, if any, is considered ``tolerable''.
, then the loss
of feasibility, if any, is considered ``tolerable''.
Termination occurs if the loss of feasibility was not
``tolerable'' and the reduction in 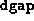 was not ``sufficient'' to
justify this loss of feasibility. In short, for the default values,
these conditions mean that we are not willing to let the algorithm
continue if the primal or dual infeasibility worsened by a factor
of 5 or more, unless the gap improved by a factor of at least 100.
These parameters attempt to achieve a judicious balance between feasibility
and complementarity by trading the former in return for the latter.
was not ``sufficient'' to
justify this loss of feasibility. In short, for the default values,
these conditions mean that we are not willing to let the algorithm
continue if the primal or dual infeasibility worsened by a factor
of 5 or more, unless the gap improved by a factor of at least 100.
These parameters attempt to achieve a judicious balance between feasibility
and complementarity by trading the former in return for the latter.
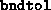
- (Default value =
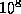 )
)
Tolerance on the norm of the solution; if 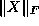 or
or 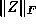 becomes
greater than
becomes
greater than 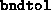 , the algorithm terminates. Unbounded primal (dual)
feasible iterates suggest that the dual (primal) program may be infeasible.
, the algorithm terminates. Unbounded primal (dual)
feasible iterates suggest that the dual (primal) program may be infeasible.
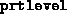
- (Default value = 1)
Determines print level;
setting this to 0 produces no output from fsdp.m, except
warnings that Matlab 4 insists on displaying that ill--conditioned
systems are being solved. This is normal near the
solution. Setting
This is normal near the
solution. Setting 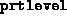 to 1 produces one line of output per
iteration (iteration number, primal and dual step lengths, primal and
dual infeasibilities,
to 1 produces one line of output per
iteration (iteration number, primal and dual step lengths, primal and
dual infeasibilities, 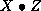 , primal and dual objective values).
Upon termination, summary information is provided by the script sdp.m
regardless of the value of
, primal and dual objective values).
Upon termination, summary information is provided by the script sdp.m
regardless of the value of 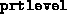 .
.
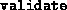
- (Default value = 0)
By default, several minor consistency checks on the dimension of the
data are performed. Additionally, if
 , fsdp.m
makes a check to ensure the initial
, fsdp.m
makes a check to ensure the initial 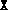 and
and 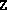 conform to the block
diagonal structure specified.
conform to the block
diagonal structure specified.




Next: Initializing the variables
Up: The script sdp.m
Previous: Preparing the data
Madhu Nayakkankuppam
Fri Mar 28 00:48:56 EST 1997
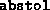 ,
, 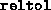 and
and 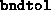 , for which
appropriate values are quite problem dependent.
All the parameters are set to their default values by calling the
routine setpars.m. The default values demand high accuracy;
the number of iterations required to meet the termination criteria is reduced
by requesting less accurate solutions.
, for which
appropriate values are quite problem dependent.
All the parameters are set to their default values by calling the
routine setpars.m. The default values demand high accuracy;
the number of iterations required to meet the termination criteria is reduced
by requesting less accurate solutions.

 (see below), then explicitly setting
(see below), then explicitly setting 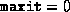 before calling the solver results in just data validation alone.
before calling the solver results in just data validation alone.

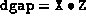 is
reduced by approximately a factor of
is
reduced by approximately a factor of 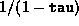 per iteration in
the last few iterations.
per iteration in
the last few iterations.
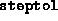
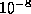 )
) , the algorithm terminates. If the infeasibility or
dgap is large, it is recommended to try restarting with
either a reduced value of
, the algorithm terminates. If the infeasibility or
dgap is large, it is recommended to try restarting with
either a reduced value of  or with
or with 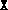 and
and 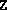 set to
larger multiples of the identity. This is done automatically when the
driver script sdp.m is used, but is not done if the the
driver script is bypassed with a direct call to the function
fsdp.m.
set to
larger multiples of the identity. This is done automatically when the
driver script sdp.m is used, but is not done if the the
driver script is bypassed with a direct call to the function
fsdp.m.
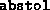
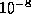 )
)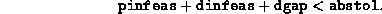
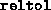
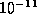 )
)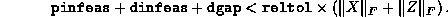
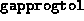
 (see below), determines when the algorithm
should terminate if significant progress is not taking place.
If
(see below), determines when the algorithm
should terminate if significant progress is not taking place.
If 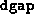 is less than the previous value of
is less than the previous value of 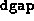 divided by
divided by
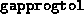 , then the progress is considered ``sufficient''. This
check is performed only when
, then the progress is considered ``sufficient''. This
check is performed only when 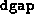 has been reduced below
has been reduced below 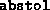 .
.

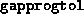 (see above),
determines when the algorithm should terminate if significant progress
is not taking place. If the new
(see above),
determines when the algorithm should terminate if significant progress
is not taking place. If the new  is less than
is less than
 times the previous
times the previous  , or the new
, or the new 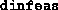 is
less than
is
less than  times the previous
times the previous 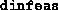 , then the loss
of feasibility, if any, is considered ``tolerable''.
, then the loss
of feasibility, if any, is considered ``tolerable''.
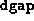 was not ``sufficient'' to
justify this loss of feasibility. In short, for the default values,
these conditions mean that we are not willing to let the algorithm
continue if the primal or dual infeasibility worsened by a factor
of 5 or more, unless the gap improved by a factor of at least 100.
These parameters attempt to achieve a judicious balance between feasibility
and complementarity by trading the former in return for the latter.
was not ``sufficient'' to
justify this loss of feasibility. In short, for the default values,
these conditions mean that we are not willing to let the algorithm
continue if the primal or dual infeasibility worsened by a factor
of 5 or more, unless the gap improved by a factor of at least 100.
These parameters attempt to achieve a judicious balance between feasibility
and complementarity by trading the former in return for the latter.
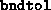
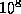 )
)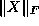 or
or 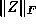 becomes
greater than
becomes
greater than 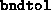 , the algorithm terminates. Unbounded primal (dual)
feasible iterates suggest that the dual (primal) program may be infeasible.
, the algorithm terminates. Unbounded primal (dual)
feasible iterates suggest that the dual (primal) program may be infeasible.
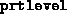
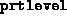 to 1 produces one line of output per
iteration (iteration number, primal and dual step lengths, primal and
dual infeasibilities,
to 1 produces one line of output per
iteration (iteration number, primal and dual step lengths, primal and
dual infeasibilities, 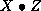 , primal and dual objective values).
Upon termination, summary information is provided by the script sdp.m
regardless of the value of
, primal and dual objective values).
Upon termination, summary information is provided by the script sdp.m
regardless of the value of 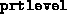 .
.
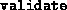
 , fsdp.m
makes a check to ensure the initial
, fsdp.m
makes a check to ensure the initial 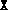 and
and 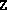 conform to the block
diagonal structure specified.
conform to the block
diagonal structure specified.