Binary (Search) Trees
Problem 1
Use lab10 IntBST workspace on Ed. Complete the four missing functions. Submit your final code to Gradescope to see if your implementation passes all the tests.
Remember to remove any debugging print statements before submitting.
(There is nothing to submit for the remaining problems in this lab.)
Problem 2
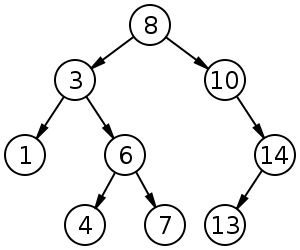
- Which of the nodes in the above tree are at level 2?
- How many nodes would have to be added to level 3 so that the number of nodes at that level is maximum?
- Assuming that the height of leaf nodes is defined to be zero, what is the height of the above tree?
- Assuming that the height of leaf nodes is defined t0 be zero, what is the height of the node with value 3?
- Recall the iterative algorithm for calculating the size of a binary tree that we discussed in class. What is the largest number of elements in the stack when the algorithm is applied to the above tree?
Problem 3
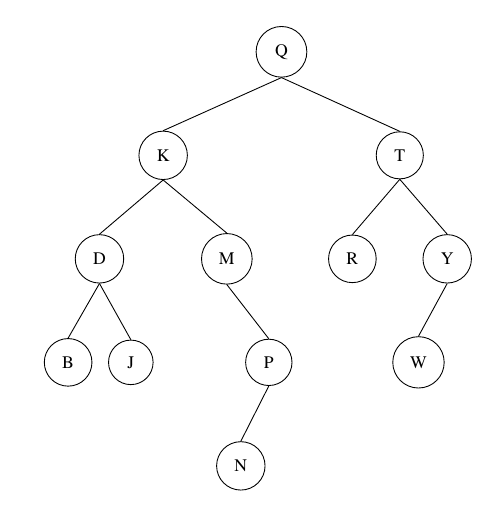
- Specify the inorder traversal of the above tree. Provide your answer as a sequence of uppercase letters with nothing in between them so them.
- Specify the preorder traversal of the above tree. Provide your answer as a sequence of uppercase letters with nothing in between them so them.
- Specify the postorder traversal of the above tree. Provide your answer as a sequence of uppercase letters with nothing in between them so them.
Problem 4
You are told that the preorder and postorder traversals of a given tree are as follows:
preorder: A B C D E F G H I
postorder: C E D B H G I F A
Construct a tree for which this is the case.
Problem 5
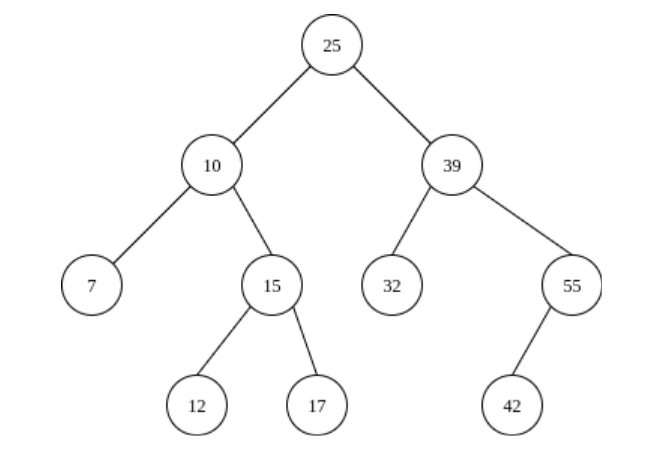
Starting with the binary search tree shown above, show what the tree will look like after each of the following operations. Assume that the remove method uses the successor when applicable. For each step modify the original tree (not the tree from the step before).
- add 21
- add 8
- add 30
- remove 7
- remove 55
- remove 39
Problem 6
Use the following tree to answer questions below
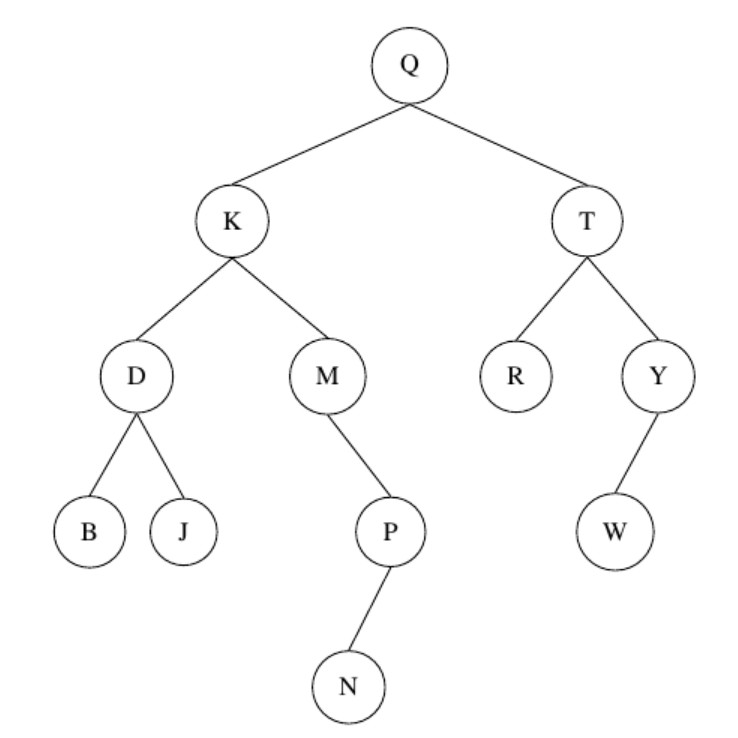
-
Which of the following specifies its preorder traversal?
- Q K T D M R Y B J P W N
- Q K D M B J P N T R Y W
- Q K D B J M P N T R Y W
- B D J K M N P Q R T W Y
- N B J P W D M R Y K T Q
- B J D N P M K R W Y T Q
- Y W T R Q P N M K D J B
- Q T Y W R K M P N D J B
-
Which of the following specifies its postorder traversal?
- Q K T D M R Y B J P W N
- Q K D M B J P N T R Y W
- Q K D B J M P N T R Y W
- B D J K M N P Q R T W Y
- N B J P W D M R Y K T Q
- B J D N P M K R W Y T Q
- Y W T R Q P N M K D J B
- Q T Y W R K M P N D J B
-
Which of the following specifies its inorder traversal?
- Q K T D M R Y B J P W N
- Q K D M B J P N T R Y W
- Q K D B J M P N T R Y W
- B D J K M N P Q R T W Y
- N B J P W D M R Y K T Q
- B J D N P M K R W Y T Q
- Y W T R Q P N M K D J B
- Q T Y W R K M P N D J B
Problem 7
Use the following tree to answer questions below

- Redraw the tree after
remove(M)is called. Use the predecessor, if applicable. - Redraw the tree after
remove(K)is called. Use the predecessor, if applicable. Start wit the original tree. - Redraw the tree after
remove(K)is called. Use the successor, if applicable. Start wit the original tree. - Is the tree an AVL tree? If not, which nodes are not in balance?
- Assume that we remove the node with value 'N'. Is the resulting tree an AVL tree? If not, which nodes are not in balance?
- Assume that we remove the node with value 'Q' using the predecessor rule when applicable. Is the resulting tree an AVL tree? If not, which nodes are not in balance?